
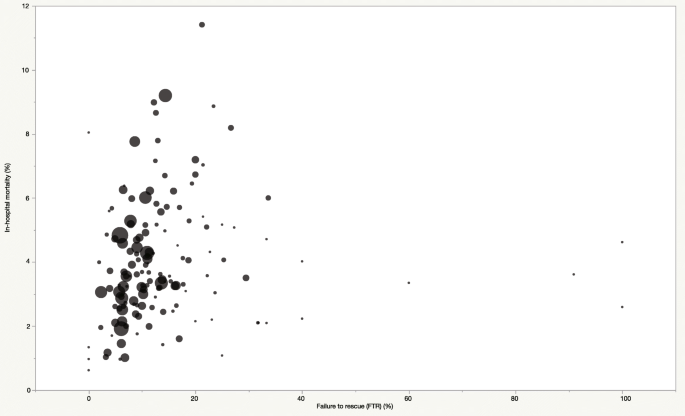

In nonoperative settings, specialized structures and processes of care are associated with improved outcomes for frail and elderly patients 15 specialized geriatric care for hip fracture patients, many of whom are frail, results in improved postoperative outcomes. 14 Frail and elderly patients require complex care due to the significant comorbidity burden, altered physiology, and cognitive issues that are common in this population. 13 For example, while complication rates do not vary substantially between different hospitals based on procedural volume, patients cared for at high procedural volume hospitals experience lower rates of mortality following postoperative complications. 11, 12 This volume–outcome relationship is often attributed to improved structures and processes of care at high-volume centers and the underlying experience and expertise of providers that volume may represent. Patients treated by hospitals and/or surgeons who perform a high volume of specific procedures tend to experience decreased rates of mortality, complications, and other adverse outcomes. 9, 10 Since the prevalence of frailty increases with age, more frail patients may be considered for elective surgery as the population ages. Frailty is an independent risk factor for postoperative morbidity, increased resource use, and mortality.
6 Frailty, an aggregate expression of risk of adverse health outcomes due to age- and disease-related deficits that accumulate across multiple domains, 7, 8 appears to be a key factor that explains this variation. 4, 5 However, despite the well-established association between advanced age and adverse events, significant outcome variation exists between older patients that is not accounted for by differences in age and comorbidity burden alone. 3 Older age is also associated with an approximately 2.5-fold increase in the risk of postoperative morbidity and mortality. 1, 2 Older patients undergo major surgery at a rate two to four times higher than younger age groups. THE populations of developed countries are aging rapidly people aged 65 yr and older are the fastest growing demographic in Western countries.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
